Your cart is currently empty!

The Risks of Expired SSL Certificates
SSL certificates are crucial for authenticating websites and ensuring secure internet traffic.
They verify a website’s identity and encrypt the data exchanged between a user’s browser and the website.
However, their effectiveness is contingent on their validity, which now, due to changes in policy by major internet entities like Apple, Google, and Mozilla, is capped at a maximum of 398 days.
This shift, initiated in 2020, aims to improve security by encouraging more frequent updates and reducing the risks associated with outdated encryption.
Why the Change?
The decision to shorten SSL certificate lifespans was made to enhance cybersecurity.
Shorter validity periods prompt more frequent updates, allowing for the implementation of the latest encryption standards and quicker responses to cyber threats.
Although managing these certificates can be challenging, the benefits of maintaining up-to-date encryption standards outweigh the administrative overhead.
What Are the Risks?
An expired SSL certificate can significantly undermine a website’s security and credibility.
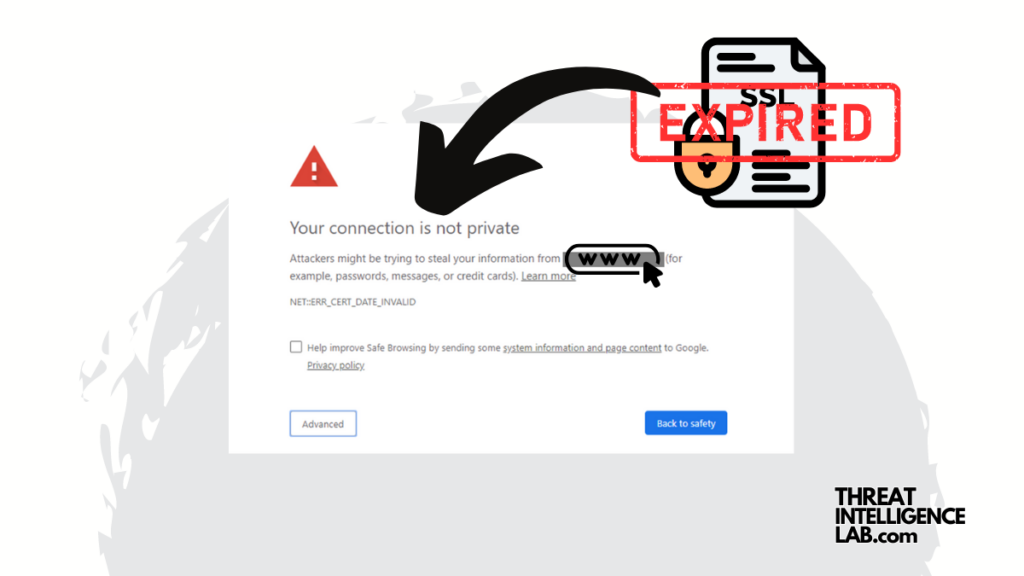
Users will receive warnings from their browsers. These warnings deter them from visiting the site. This situation can potentially lead to a loss of customer trust and revenue.
Furthermore, expired certificates can cause service outages and make websites more susceptible to cyberattacks, including man-in-the-middle (MITM), POODLE, BEAST, and CRIME attacks, all of which exploit vulnerabilities in outdated SSL/TLS protocols.
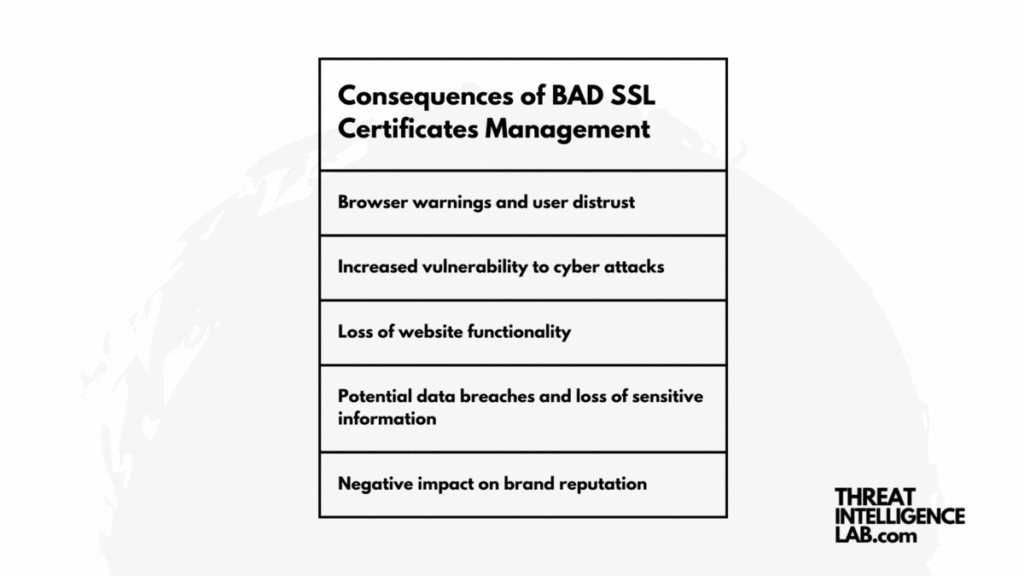
The Consequences of Neglect
Instances of service disruptions due to expired SSL certificates are not rare.
High-profile cases, such as outages experienced by GitHub and Spotify, highlight the tangible impacts of such oversights, affecting millions of users and tarnishing reputations.
Renewal Challenges
While there are numerous tools available to assist with certificate management, the task can be daunting.
This is especially true for large organizations with multiple websites and domains.
The main challenge lies in maintaining an accurate inventory of all assets requiring certificates.
Overlooked or unknown domains can lead to unprotected sites and the associated risks.
Recommendations for Effective SSL Management
I suggest implementing thorough certificate management practices. This involves regularly auditing digital assets, using automated renewal tools, and promoting collaboration between IT and security teams to keep all certificates current.
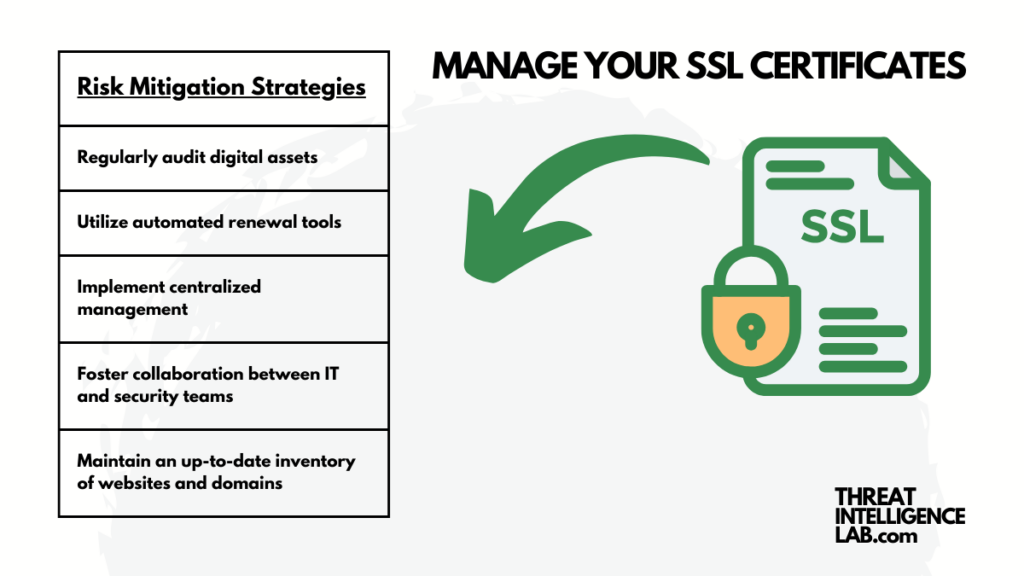
To minimize risks, it’s crucial to establish a strong process for monitoring and renewing SSL certificates before they expire.
In summary, although policy changes and ongoing SSL certificate management may pose challenges, businesses cannot ignore their significance in maintaining website security and user trust.
By adopting strict management practices, businesses can safeguard themselves from the considerable risks linked with expired SSL certificates.