In my experience as a cybersecurity expert, I’ve seen a lot of clever tricks from cybercriminals. But a recent trend has caught my attention – it’s a game-changer in the world of fake IDs and online security.
As reported by Joseph Cox at 404media.co, there is an underground website named OnlyFake that is using artificial intelligence to create super realistic fake IDs for just $15. This is big news, especially for countries like The Netherlands where there are strict KYC (Know Your Customer) checks.
Research done by Jonathan Spedale shows that the OnlyFake platform does not make use of AI. Rather they make use of image editing tools. To read the full research. Follow this link. You do need a LinkedIn profile for this.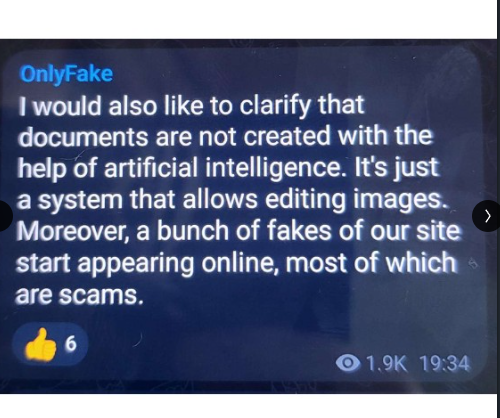
AI-Generated Fake IDs
Let’s dive into what’s happening. OnlyFake uses something called “neural networks” to make fake IDs that look incredibly real.
This isn’t just a minor tweak in the world of fake IDs; it’s a major shift. Imagine, for a moment, being able to create a highly convincing ID for just a few bucks.
That’s what we’re dealing with here.
Finance services and Banking
The arrival of AI-generated fake IDs, like those from OnlyFake, presents a multifaceted threat for the financial sector.
Let’s explore the specific risks and how they extend to the burgeoning fintech industry.
Traditional Banking: A Vulnerable Target
Banks have always been prime targets for fraudsters, and the introduction of AI-generated fake IDs exacerbates this vulnerability.
These institutions traditionally rely on physical forms of ID for customer verification.
With the advent of AI technology capable of creating highly convincing fake IDs, the entire foundation of their KYC (Know Your Customer) processes is stressed.
Fraudsters use these IDs to open bank accounts, which can then be used for a range of illicit activities, from basic identity theft to more complex schemes like loan fraud.
This leads to financial losses for the banks but also damages their reputation and erodes customer trust.
The Impact on Fintech
The fintech sector, which includes everything from online banking platforms to mobile payment apps, is particularly at risk. Fintech companies often pride themselves on their ease of access and user-friendly processes, which can make them attractive targets for cybercriminals using AI-generated IDs.

Fintech firms generally have less stringent regulatory requirements than traditional banks, which might lead to less rigorous ID verification processes.
This can be exploited by fraudsters using sophisticated fake IDs, enabling them to bypass checks more easily.
For instance, they could create accounts to conduct fraudulent transactions, manipulate peer-to-peer lending platforms, or engage in credit card fraud.
Money Laundering Risks
Another major concern is money laundering1. With access to seemingly legitimate banking services, criminals funnel illicit funds through various accounts, using fake IDs to obscure their tracks.
This poses a threat to the integrity of financial institutions and also has broad implications for global financial security.

Identity Theft and Consumer Fraud
From a consumer perspective, the risk of identity2 theft looms large.
Fraudsters could potentially create bank accounts or apply for credit cards in someone else’s name, leading to significant personal financial loss and credit damage.
Staying One Step Ahead with Cyber Threat Intelligence
CTI is all about understanding and anticipating the tactics, techniques, and procedures of adversaries. In the context of AI-generated fake IDs, CTI can be incredibly valuable.
- Why Data Breach Report Feeds Are Important
- The Top 10 Essential Log Sources for IT Monitoring
- Dark Web Cybercrime Forums You Should Monitor
- How to Parse and Use VirusTotal feeds
- Getting The Most Out Of URLscan.io
Anti-Fraud Detection Mechanisms
Anti-fraud detection mechanisms are crucial in identifying and preventing fraudulent activities in real-time.
Here’s how they can help:
Adaptive Risk-Based Approaches
Adopting a risk-based approach is essential. This means the level of scrutiny3 applied during the verification process is proportional to the risk associated with the customer.
High-risk customers or transactions would undergo more rigorous checks, whereas low-risk ones would have a streamlined process. This approach ensures that resources are efficiently allocated, focusing more on where the risk of fraud is higher.

Anomaly Detection
By continuously monitoring for unusual activities or transactions, these systems can flag potential fraud.
For example, if a new account immediately engages in high-value transactions, it could trigger an alert for further investigation.Behavioral Biometrics
This involves analyzing user behavior such as typing patterns, mouse movements, and even device handling characteristics.
Such biometrics help in distinguishing between a legitimate user and a fraudster, even if the fraudster has a convincing fake ID.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds additional layers of security beyond just ID verification.
This can include something the user knows (like a password), something the user has (like a phone), and something the user is (like a fingerprint or facial recognition).
Machine Learning Algorithms
These algorithms can learn from past incidents of fraud and become more adept at detecting similar attempts in the future.
They can analyze vast amounts of data to identify subtle patterns indicative of fraudulent activities.

Integration with KYC Processes
The integration of Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) and anti-fraud mechanisms within KYC processes represents a critical evolution in the fight against increasingly sophisticated cyber threats, particularly the challenge posed by AI-generated fake IDs.
In the past, traditional KYC checks were largely effective, but as technology advances, so too do the methods of those intent on committing fraud.
This new landscape necessitates a more dynamic approach to identity verification and customer due diligence.
Enhancing Accuracy and Reliability
The primary benefit of incorporating CTI and anti-fraud mechanisms into KYC processes lies in the significant enhancement of accuracy and reliability.
Traditional methods, often reliant on manual checks of documentation, are increasingly susceptible to the high-quality forgeries made possible by AI technologies.
CTI can provide real-time data and analysis on emerging fraud techniques, enabling institutions to adapt their verification processes swiftly and effectively. This means that fraudulent attempts using sophisticated fake IDs can be detected with greater accuracy.
Proactive Threat Detection
Integrating these advanced tools allows for a more proactive approach to threat detection. Traditional KYC processes are predominantly reactive, relying on spotting discrepancies after they have occurred.
In contrast, CTI and advanced anti-fraud systems can anticipate and identify potential threats before they materialize into actual fraud.
Comprehensive Risk Assessment
Moreover, this integration facilitates a more comprehensive risk assessment. CTI provides deeper insights into the types of threats and the behaviors of fraudsters, enabling financial institutions to evaluate the risk level of certain transactions or activities more effectively.
Building Customer Trust
Enhancing KYC processes with CTI and anti-fraud mechanisms also plays a significant role in building and maintaining customer trust. In an era where consumers are increasingly aware of identity theft and financial fraud, robust KYC practices are a strong signal of an institution’s commitment to protecting its customers’ interests.
This helps in retaining existing customers and attracting new ones who value security and privacy.

Compliance and Regulatory Alignment
Finally, this enhanced approach ensures better compliance with regulatory requirements. Regulatory bodies worldwide are updating their guidelines to reflect the changing nature of financial crimes. Integrating CTI and anti-fraud mechanisms into KYC processes helps institutions stay aligned with these evolving regulations, avoiding potential legal pitfalls and reputational damage.
Common KYC attacks
Criminals have developed a range of sophisticated attacks to circumvent KYC (Know Your Customer) checks, exploiting vulnerabilities in systems and procedures. Here’s a list of common attacks, including the use of AI-generated fake IDs:
Conclusion
In conclusion, it’s crucial to recognize that the threat landscape, especially with advancements like AI-generated fake IDs, is constantly evolving. Staying informed and vigilant is not just a one-time effort; it’s an ongoing battle. As technologies advance, so do the methods employed by cybercriminals, making it imperative for individuals, businesses, and institutions to keep pace with these changes. The fight against such sophisticated threats requires continuous learning, adapting, and innovating in our approaches to cybersecurity.